In Dec. 2014, an outbreak of E. coli O55 was identified in Dorset, U.K. with at least 31 sickened. Public Health England (PHE) and local environmental health officials investigated and found nothing, other than cats were also being affected.
 Tara Russell of Bournemouth Echo reports again this week that a review into the outbreak in Dorset was carried out, health chiefs have insisted – but the report is not available to the public.
Tara Russell of Bournemouth Echo reports again this week that a review into the outbreak in Dorset was carried out, health chiefs have insisted – but the report is not available to the public.
Public Health England (PHE) says the public can only request to see the report detailing exactly what happened when 31 people contracted the O55 strain between July 2014 and November 2015 through a Freedom of Information request.
Families including some whose children have been left with lifelong health complications say they did not know the review existed and have branded it ‘disappointing and disgusting’ they have been kept in the dark.
The Daily Echo has lodged an official FOI request on behalf of the affected families and will receive a response in July.
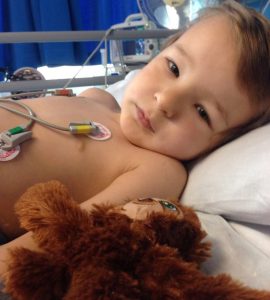
Nurse Jessica Archer, who today suffers crippling head pains, fatigue and depression while her nephew Isaac Mortlock (right) endures severe seizures, must be peg fed every night and will need a kidney transplant as a result of the outbreak, said: “Without the Daily Echo we wouldn’t even know this report even existed and we are very interested to see it and we have the right to know. The families affected have so many unanswered questions and have to live with the effects of this outbreak forever but yet again we feel Public Health England are trying to sweep it under the carpet and hope that it will just go away.
“It is disappointing and disgusting this report has not already been made public let alone having to wait and wait still. We feel there have been a series of failures and this is the latest.”
The news comes after Jessica last month called for PHE to be held to account telling how her and her five-year-old nephew’s Isaac Mortlock’s lives have changed irreversibly, and accused the organisation of ‘a cover up.’
In response, PHE told the Daily Echo it carries out ‘routine outbreak reviews once investigations have ended’, adding it is ‘a learning organisation and reflects on outbreaks to identify lessons learnt and to continually improve our response.’
However at the time, the organisation refused to tell the Daily Echo exactly which lessons were learned.
 It was only following a further request from this newspaper, PHE said a report was compiled however it has not been available to the public.
It was only following a further request from this newspaper, PHE said a report was compiled however it has not been available to the public.
A spokesman said: “This report was not intended for external publication – it’s not standard procedure to publish outbreak reports externally due to patient confidentiality – however if interested parties would like to request a copy they can do this via our Freedom of Information portal.”
That’s bullshit.
Outbreak investigations are routinely published while ensuring patient confidentiality.
Families say it is the latest in a string of ‘failures’ by Public Health England.
A spokesman from PHE added: “As with all outbreaks, PHE Health Protection Team ensured throughout their investigation that those affected were kept informed of any information that was uncovered at that time.”
That’s also bullshit.
And why UK health types feature prominently in our paper on when to go public for the benefit of public health.
Three years seems a bit long.
Going public: Early disclosure of food risks for the benefit of public health
Mar.17
NEHA, Volume 79.7, Pages 8-14
Benjamin Chapman, Maria Sol Erdozaim, Douglas Powell
http://www.neha.org/node/58904
Often during an outbreak of foodborne illness, there are health officials who have data indicating that there is a risk prior to notifying the public. During the lag period between the first public health signal and some release of public information, there are decision makers who are weighing evidence with the impacts of going public.
Multiple agencies and analysts have lamented that there is not a common playbook or decision tree for how public health agencies determine what information to release and when. Regularly, health authorities suggest that how and when public information is released is evaluated on a case-by-case basis without sharing the steps and criteria used to make decisions.
Information provision on its own is not enough. Risk communication, to be effective and grounded in behavior theory, should provide control measure options for risk management decisions. There is no indication in the literature that consumers benefit from paternalistic protection decisions to guard against information overload. A review of the risk communication literature related to outbreaks, as well as case studies of actual incidents, are explored and a blueprint for health authorities to follow is provided.
